Whether you’re a seasoned professional, just getting into the welding profession or a passionate welding DIYer and hobbyist, it can’t hurt to brush up on some tips. Detailed below are tips for a couple of different welding methods, in addition to some general safety tips and reminders to ensure that your welding minimizes harm to yourself, others around you and your work setting.
Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding
Also known as gas metal arc welding (GMAW) or metal active gas (MAG) welding, MIG welding relies on the continuous feeding of a spool of hot metal wire to melt two components of metal together. MIG welding is typically quicker and easier to do than TIG welding, which we’ll get to in a moment.
Make Sure Your Wire Is Feeding Properly
Choosing the correct drive roll is crucial to your wire’s continuous feed during the course of the MIG welding process. Not enough tension can result in a poor feed. Bends in the wire can also lead to lost tension, so be sure to keep the gun as straight as you possibly can.
Know the Correct Specs for the Job and Your Equipment
This includes knowing which kind of gas best accommodates your wire, be it argon, carbon dioxide or a mix of the two. The kind of job you’re working on dictates specific kinds of wires and gas. Additionally, the contact tip recess you use varies depending on the type of project you hope to complete. Generally, you want to increase the size of the recess in conjunction with the current.
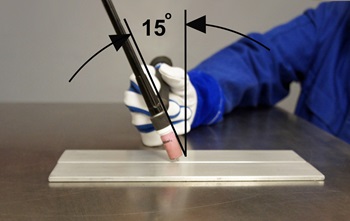
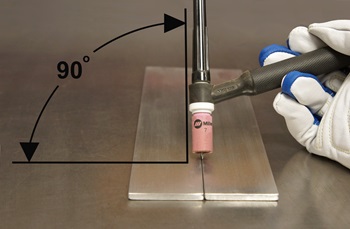
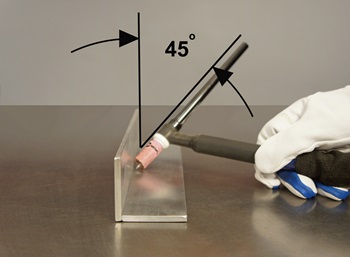
Point Your Wire at the Leading Edge of the Weld Puddle
To ensure best accuracy during the MIG welding process, keep your electrode pointed at the leading edge (i.e., toward the metal that has not yet been welded) of the weld puddle or pool. If you’re welding in an unusual position, you should use a wire with a smaller diameter to keep the weld pool small and minimize drip.
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding
TIG welding, otherwise known as gas tungsten arc welding (GTA or GTAW), is a process that uses a tungsten electrode aided by a shielding gas, usually argon or helium, to fuse metal. This process is more precise than MIG welding, but also more time-consuming.
Choose the Right Rod Size for the Job
Ideally, the thickness of the rod should match the thickness of the metal you’re working on. You wouldn’t want to use a thick rod — say, 1/8” in diameter — on a weak piece of metal because you could easily put a hole through it with the sheer heat of the rod relative to the sheet. One benefit of TIG welding is the increased precision, but you still have to use the right tools to reap that advantage.
Clean Your Metal Before TIG Welding
If the metal you wish to TIG weld is rusted, scaled or painted, you’ll want to grind it down before you get started. Unlike MIG welding, TIG welding is more easily compromised if the metal is not clean. Polishing the metal alone will not suffice and can result in a tacky-looking finished product if you elect to take shortcuts in preparation.
Make Sure to Extend Your Tungsten Electrode to the Right Length
Having the tip of your electrode positioned at the proper length is crucial to the final product when you’re TIG welding. If the tip is not sticking out far enough, you won’t be able to see it — or, consequently, where you’re welding the metal. On the other hand, if the tip is out too far from the cup, the heat of the torch won’t be concentrated enough around the area you’re trying to weld and will probably end up melting your rod into the weld.
Safety Tips for Welding of All Kinds
It could be argued that many of the tips already presented fall into the category of safety tips, which is true. Having a working knowledge of the right equipment certainly contributes to minimizing the number of personal injuries experienced by welders. However, there are additional measures that should be taken to further reduce such risks.
Have a Spotter
It’s always a good idea to have someone watch you while you’re welding, if you can. This is especially true when welding around flammable materials. Having another set of eyes in the vicinity can reduce the risk of fires in the event that sparks get out of hand. Also, make sure to familiarize yourself with your surroundings and locate the nearest fire exits.
Personal Protective Equipment
Referred to as PPE for short, personal protective equipment is your first and last line of defense against heat, sparks and other hazards associated with welding. Wearing a mask with a shade dark enough to sufficiently protect your eyes from the brightness of the arc is an absolute must. You should also wear flame-retardant cotton or leather clothing with long sleeves and long pants, as well as fire-resistant gloves, to protect your extremities from sparks. Additional eye protection beneath the mask is also recommended, on top of some sort of ear protection to prevent impalement by debris.
Check Your Ventilation
It’s of the utmost importance that you are able to breathe clean air while you weld. You should always wear an approved respirator to protect your lungs against the fumes of dangerous metal oxide compounds. If you experience issues with your ventilation system, stop welding and address the problem immediately.
Discover the Summit Welding Difference
Welding Some of you readers are probably wondering how to go about breaking into a welding career of your own. The answer is simple. It all begins with a quality trade school education that will provide you with the education you need to start welding and give you the chance to be on your way to a rewarding career. Summit College’s welding program could be just the program for you.
Summit College is dedicated to providing students with the personal attention they need to succeed in learning the welding trade. As a student in Summit College’s welding program, you will be immersed in the basics of welding upon which your career in the industry will be built. Summit’s comprehensive welding curriculum includes courses in such subjects as:
Shielded Metal Arc Welding
Flux Cored Arc Welding and Blueprint Reading
SMAW Pipefitting and Layout
Fabrication and Repair
Career Development
Summit’s program will help prepare you for a welding career in various settings, such as the automotive, construction, trucking and railroad, and ironworks industries and more.
Summit College is proud to offer its nine-month welding program at its Colton, El Cajon and Santa Ana campuses in California. To accommodate the most potential students, day, afternoon and night classes are available to help you fit your education into your busy daily life. You can also benefit by being able to finish the program and begin working sooner than your peers who may have opted for four-year programs at a traditional college or university.
The instructors in Summit’s welding program are experienced and knowledgeable professionals who provide students with individual attention to ensure they learn the necessary welding skills. Students learn the ins and outs of the profession in classroom and laboratory settings.
Summit College also offers students career assistance that can help you find employment, including resume help, mock interviews and externships. This wealth of resources can help you make the most of the openings in the welding field.
What are you waiting for? Combine your passion for the trade with a program dedicated to helping you achieve your dreams and create a meaningful career by visiting https://summitcollege.edu/ today.